Mark Crawford, Contributing Writer07.22.21
The goal of metal injection molding (MIM) and metal additive manufacturing (metal AM) is the same—to make durable, high-quality metal components, implants, instruments, and other devices. Both methods offer medical device manufacturers (MDMs) and their contract manufacturers (CMs) an alternative to traditional machining.
MIM is well-suited for small, complex geometries and intricately shaped components. It is also a good option for manufacturing medium- to high-volume parts for medical devices for laparoscopic surgeries and other high-volume applications, such as surgical instruments.
“We have used MIM successfully for over 20 years to manufacture millions of parts yearly for single-use surgical instruments, including powered device drive chains, end effectors, connectors, and other applications,” said Steve Santoro, executive vice president for MICRO, a Somerset, N.J.-based full-service contract manufacturer of precision medical devices and provider of injection/insert/metal injection molding services. “MIM is versatile and low-risk from a manufacturing standpoint and used broadly across a range of industries.”
MIM is also a highly scalable and cost-effective metal manufacturing technique, which is one reason the global market for MIM “is growing at a rate of 7.5 percent annually, as more industries adopt the process for an expanding range of applications,” added Nick Eidem, director of business development for Advanced Powder Products, a Philipsburg, Pa.-based provider of metal injection molding and 3D metal printing (3MP).
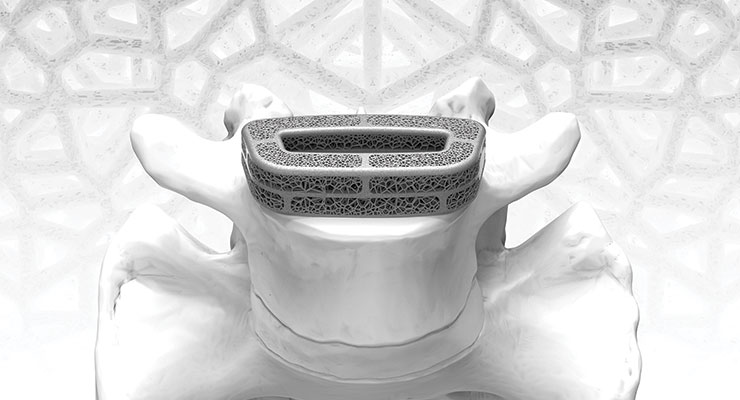
For metal AM, medical device applications continue to expand as the process becomes more widely accepted as a viable alternative to traditional machining. AM is especially popular in orthopedics because of its ability to create monolithic, porous structures that can promote bony in-growth. “In addition, metal AM eliminates the need for tooling, which helps to reduce costs,” said Jeph Ruppert, director of the application innovation group for 3D Systems, a Rock Hill, S.C.-based provider of additive manufacturing solutions. “Metal AM also is a great solution for the production of personalized implants and instruments because of the design freedom it can provide.”
The most utilized metal AM processes for medical device production are powder bed fusion (PBF) technologies, which weld layers of metal powder together utilizing a high energy source, typically a laser or electron beam. Titanium is the metal of choice for most AM applications.
“Metal AM is used mostly for manufacturing titanium alloy implantable devices with integrated lattice or porous structures that encourage osteointegration,” said Ryan Kircher, senior additive manufacturing engineer for rms Company, a Coon Rapids, Minn.-based contract manufacturer for medical devices. “Companies are manufacturing these types of devices for a variety of applications throughout the body, including spine, knee, hip, and extremities.”
There is also a market for AM stainless steel plates and instruments, but is limited to mostly small-run and special projects due to higher costs. Other materials include cobalt-chrome (CoCr) for implants.
Latest Trends
Titanium MIM is becoming the preferred manufacturing method for products with long lifecycles in the market and large annual production volumes. Also, because of COVID-19, more MDMs are moving toward single-use devices, which are a good match for MIM.
Injection molding is advantageous because of its shorter timelines. For standard components, “in a month, we can produce 30 to 40 molds,” said Santoro. “It takes one to two weeks to create samples, two to three weeks for prototype tools, and upwards of four to six weeks for production tools. Time frames can be condensed by using reliable vendors to build the molds.”
Projects often require multiple tools, and delays can occur at the beginning when deciding on a mold and reviewing designs to ensure functionality will not be impacted. MICRO uses AM for tooling but not prototype builds due to the large difference in surface roughness and dimensional capability. “AM is okay for ‘touch and feel’ samples,” said Santoro. “However, when functional or life testing is needed, no conclusions can be made using AM parts when the device will eventually have MIM or machined parts.”
The orthopedic sector continues to adopt 3D printing for a growing range of applications—in part because AM systems are becoming more affordable and can produce parts more quickly than before. Used initially for spine applications, AM is now accepted across multiple platforms, including more critical applications in orthopedics such as tibial trays and femoral implants.
“The trends we see are directly related to the markets in which our clients serve,” said Brian McLaughlin, president of Amplify Additive, a Scarborough, Maine-based provider of additive manufacturing for titanium orthopedic implants. “If you are a spine company, you need to have a 3D-printed solution to stay competitive. Uncemented solutions for total joints continue to grow, which means more 3D-printed tibial trays for total knees. I think that 3D-printed acetabular cups are also to be expected in today’s market.”
There is growing interest in metal binder jet printing, especially for titanium. Binder jet printing is similar to MIM and offers a competitive alternative for certain high-volume applications. Binder jet printing is not a mature market yet—however, in December 2020, Ex One announced its binder jet 3D printing system that allows reactive materials to be processed, including metals; a controlled-atmosphere model of its X1 160Pro extra-large production metal printer will be available in 2022 for aluminum and titanium production.1
MIM versus Metal AM
Compared to plastic components, metal as a raw material is costly to manufacture and there are many processes available for fabricating metal components. “The least expensive component is usually the raw materials,” said Santoro. “When additional steps are added, costs rise. The key is to pick the best process for each component. Having detailed knowledge of the costs and processing associated with as many of these technologies as possible makes the job easier.”
Metal injection molding combines plastic injection molding with metal powder fusion. MIM is often the method of choice when small or complex parts are required that cannot be efficiently manufactured using any other methods. Injection molding can be automated when high volumes and consistent quality are needed. “MIM is ideal for small, complex geometries and intricately-shaped parts,” said Santoro. “Post-MIM computer numerical control [CNC] machining can be used to achieve tight tolerances.”2
MIM parts are strong and can be bent, welded, hardened, and heat-treated like other wrought materials. A wide variety of metals can be processed with MIM, including stainless steel, steel alloys, iron-nickel alloys, cobalt alloys, tungsten alloys, and ceramics.
Since only a single mold is required to make a part using MIM, the process is highly repeatable and produces parts consistent in size, shape, and strength. Finished parts are relatively strong for their size, often above 95 percent density. According to Fast Radius, a Chicago, Ill.-based contract manufacturer that provides both AM and MIM services to the medical device industry, “because molds can cost anywhere from $50,000 to $100,000, which could be prohibitively expensive for low-volume production runs, MIM makes financial sense for annual volumes over 50,000 with a long production lifecycle.”3
Both MIM and 3MP have surface finishes that, in their raw states, are inferior to machined components. In addition, dimensional control can often be an issue. “In the raw state, MIM surface finish and dimension control are superior to those of 3MP,” said Eidem. “Many MIM and 3MP manufacturers have secondary machining and surface finishing capabilities that can close the gap between these two technologies.”
MIM typically comes with a longer qualification timeline when compared to other manufacturing processes. “Design iterations can also stretch timelines and budgets,” continued Eidem. “Because of this, OEMs often default to machined components and forego the long-term cost benefit of MIM. OEMs are constantly looking for ways to reduce this qualification timeline and iteration process to capitalize on the advantages of MIM. 3MP can be used to drastically reduce this timeline and iteration process.”
For example, Advanced Powder Products has its own 3D printing technology, Printalloy, that uses the same MIM powder and processing conditions as production components, without the need for tooling. This allows the engineering team to run experiments prior to production tooling being built. “These experiments help develop the process concurrently, saving time and increasing qualification speed,” said Eidem.
Engineers often use metal AM when they need to create specialized parts that require high-strength characteristics or have intricate design features. Metal AM does not require molds, which provides designers with more creative possibilities for shape, tolerance, and functionality. The main advantage of powder bed fusion is its ability to produce complex lattice and porous structures. These types of complex structures cannot be achieved using MIM or other manufacturing processes. However, the disadvantages of PBF are higher cost-per-part and lower volume production capability.
“Conversely, the advantage of MIM is that it is cost-effective and can produce high volumes,” said Kircher. “Products with complex structures are best suited to PBF, whereas simpler structures in need of high-volume production are better suited to MIM.”
Another important advancement in laser powder bed fusion technology is the development and deployment of programmable lasers as the power source. Instead of using a focused columnar laser, the density of the laser energy can be distributed into a shape such as a ring. “This advancement allows for significant increases in manufacturing speed and will also enable manufacturers to print new alloys that were previously difficult or impossible to produce,” said Olson.
The biocompatibility of laser powder bed fusion methods has also improved due to the elimination of requirements for binders.
Software Advances
Additive manufacturing of implants and surgical instruments accelerates the product development lifecycle and lowers inventory costs compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. An area of advancement that has greatly enabled MDMs and their contract manufacturers to fully realize the advantages of PBF is the development of design software. “Advanced software enables the design and production of complex implants and instruments with very fine feature resolutions,” said Ruppert.
“The next generation in orthopedic implant designs will utilize highly advanced software programs and are mathematically driven,” said Adam Clark, CEO for Tangible Solutions, a Fairborn, Ohio-based contract manufacturer of 3D-printed titanium orthopedic implants. “Now that the sky is the limit with new software capabilities, customers are getting creative and turning dreams into intentionally functional models.”
Improvements in design software include image synthesis or rendering, residual stress analysis, and real-time build simulation, all integrated into one software product. Improvements in computing power, combined with clever software solutions, now allow designers to create structures with multiple layers of additional complexity.
For example, 3D Systems has made significant upgrades to its 3DXpert software product. Improvements to porous structure generation using a graphical model allow for rapid generation and adjustments to porous structures used in medical devices. “Build simulation has also improved dramatically in recent years, which decreases the number of iterations and improves first-time right yields,” said Ruppert.
Now that MDMs and CMs have become deeply experienced with the laser powder bed fusion process, they are much better at predicting outcomes, which shortens the development cycle. As a result, engineers can evaluate designs for manufacturability, make necessary adjustments, and implement new product lines relatively quickly. “In contrast, with metal injection molding and binder jet printing, there is a lot more non-recurring engineering [NRE] and development that must happen during the development stage, because it involves de-binding and sintering processes that can introduce significant changes to the geometry of the part,” said Kircher. “It is an iterative process that creates the geometry needed in the final product. With PBF, you can go from prototype to finished part quickly. With MIM, however, NRE cost must be factored into the cost and project timelines.”
Another cost consideration with MIM is tooling. For example, many medical engineers think titanium MIM is prohibitively expensive, especially upfront tooling. However, for high-volume MIM applications, tooling costs are generally not a barrier—they are typically recovered within the first year of production due to part price savings. “Titanium MIM is in a class of its own for small parts in high volumes above 10,000 pieces annually,” said Mark Mielke, vice president of sales and marketing for Praxis Technology, a Queensbury, N.Y.-based provider of titanium metal injection molding. “AM is leading when it comes to prototyping and larger parts, especially in low volumes.”
Combining Forces
Metal injection molding and metal AM are not truly competitive processes because they address different application spaces within the medical device market. “MIM is better suited for higher-volume small parts, but it is less precise,” said Ruppert. “You cannot achieve the same isotropic values as you can with AM. Metal AM is better for producing larger, fine-featured parts that deliver the best mechanical properties.”
During product development, companies can become too machine-focused. When MDMs start designing, they may design more for the output of the machine process instead of designing for clinical achievements. Engineers may not realize that, even though metal AM and MIM are distinctly different methods that have their own preferred production scenarios, they can complement each other nicely when producing multiple parts and/or instrumentation for an entire implant system.
“When producing a new implant system, there are guides, instruments, cases, and packaging that go with the implants,” said Troy Olson, director of operations for the additive manufacturing division at rms Company. “Having the capabilities of both PBF and MIM to create these different pieces can reduce system launch time. If you know the best way to manufacture each component in an entire implant system, and have the capability to do so, the two methods complement each other well. You can also help the OEM choose the best manufacturing solution for its needs.”
Cobalt Extreme, an Australian company, has developed a process that builds a metallic endoskeleton using 3D printing and then injection molds a special polymer around that skeleton. Originally developed for oil field applications, the company realized it had potential for other markets, including medical devices.4
“The injection molded polymer in and around the metal endoskeleton is not conductive and becomes an insulator,” said David Nommensen, director of Cobalt Extreme. “In addition, other benefits of the injection-molded material include abrasion resistance, resilient deformability, cost, impact resistance, corrosion and chemical resistance, color, service temperature, and low weight. A metal endoskeleton adds mechanical strength to a polymer—think reinforced concrete.”4
Mitsubishi Chemical Advanced Materials, in partnership with AddiFab, a Danish company, has developed a new process called freeform injection molding, based on 3D-printed injection mold inserts. This allows injection molders to make the same types of products as 3D printing, but with the superior strength in finished parts that traditional injection molding provides.5
“Freeform injection molding creates injection-molded objects with the same design freedom offered by conventional 3D-printing,” said Lasse Staal, CEO for AddiFab. “At the same time, we have brought 3D-printing lead times and start-up costs to the injection molding industry, without compromising choice of materials.”5
The freeform injection molding process consists of five steps:
This process could “be especially useful for rapid and inexpensive injection mold prototyping,” said Kerry Stevenson, founder of Fabbaloo, an additive manufacturing news source that tracks the latest developments in 3D printing and AM. “Normally, the process of injection molding first involves the creation of a metal mold, a very expensive and time-consuming process that is only worth doing if there is an expectation its cost will be defrayed over many thousands or even millions of units. This technology will make it possible to inexpensively produce objects virtually identical to proposed injection molded versions, without the cost of preparing the metal mold.”6
By keeping production costs down, the freeform injection molding process could allow a business to go into low-volume production for a product that later could be switched to a proper metal mold for mass production injection molding when demand calls for it. “Freeform injection molding works with not only thermoplastics, but also with metal injection molding and ceramics as well,” added Stevenson. “This opens up the possibility of using virtually the entire worldwide catalogs of such industrial materials in the process.”6
Medical device manufacturers can utilize a variety of methods for producing parts, medical devices, and instruments, including complex ones for surgical procedures such as laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery. According to Santoro, the key is to choose the best process for the component being created. MIM and metal AM each have their merits.
“A full-service contract manufacturing organization with a series of metal fabricating operations needed for surgical instruments, including critical cleaning operations, must contemplate several aspects, including cost, materials, and volume needed before determining which process will best meet the customer’s goals for each project,” said Santoro.
References
Mark Crawford is a full-time freelance business and marketing/communications writer based in Madison, Wis. His clients range from startups to global manufacturing leaders. He also writes a variety of feature articles for regional and national publications and is the author of five books.
MIM is well-suited for small, complex geometries and intricately shaped components. It is also a good option for manufacturing medium- to high-volume parts for medical devices for laparoscopic surgeries and other high-volume applications, such as surgical instruments.
“We have used MIM successfully for over 20 years to manufacture millions of parts yearly for single-use surgical instruments, including powered device drive chains, end effectors, connectors, and other applications,” said Steve Santoro, executive vice president for MICRO, a Somerset, N.J.-based full-service contract manufacturer of precision medical devices and provider of injection/insert/metal injection molding services. “MIM is versatile and low-risk from a manufacturing standpoint and used broadly across a range of industries.”
MIM is also a highly scalable and cost-effective metal manufacturing technique, which is one reason the global market for MIM “is growing at a rate of 7.5 percent annually, as more industries adopt the process for an expanding range of applications,” added Nick Eidem, director of business development for Advanced Powder Products, a Philipsburg, Pa.-based provider of metal injection molding and 3D metal printing (3MP).
For metal AM, medical device applications continue to expand as the process becomes more widely accepted as a viable alternative to traditional machining. AM is especially popular in orthopedics because of its ability to create monolithic, porous structures that can promote bony in-growth. “In addition, metal AM eliminates the need for tooling, which helps to reduce costs,” said Jeph Ruppert, director of the application innovation group for 3D Systems, a Rock Hill, S.C.-based provider of additive manufacturing solutions. “Metal AM also is a great solution for the production of personalized implants and instruments because of the design freedom it can provide.”
The most utilized metal AM processes for medical device production are powder bed fusion (PBF) technologies, which weld layers of metal powder together utilizing a high energy source, typically a laser or electron beam. Titanium is the metal of choice for most AM applications.
“Metal AM is used mostly for manufacturing titanium alloy implantable devices with integrated lattice or porous structures that encourage osteointegration,” said Ryan Kircher, senior additive manufacturing engineer for rms Company, a Coon Rapids, Minn.-based contract manufacturer for medical devices. “Companies are manufacturing these types of devices for a variety of applications throughout the body, including spine, knee, hip, and extremities.”
There is also a market for AM stainless steel plates and instruments, but is limited to mostly small-run and special projects due to higher costs. Other materials include cobalt-chrome (CoCr) for implants.
Latest Trends
Titanium MIM is becoming the preferred manufacturing method for products with long lifecycles in the market and large annual production volumes. Also, because of COVID-19, more MDMs are moving toward single-use devices, which are a good match for MIM.
Injection molding is advantageous because of its shorter timelines. For standard components, “in a month, we can produce 30 to 40 molds,” said Santoro. “It takes one to two weeks to create samples, two to three weeks for prototype tools, and upwards of four to six weeks for production tools. Time frames can be condensed by using reliable vendors to build the molds.”
Projects often require multiple tools, and delays can occur at the beginning when deciding on a mold and reviewing designs to ensure functionality will not be impacted. MICRO uses AM for tooling but not prototype builds due to the large difference in surface roughness and dimensional capability. “AM is okay for ‘touch and feel’ samples,” said Santoro. “However, when functional or life testing is needed, no conclusions can be made using AM parts when the device will eventually have MIM or machined parts.”
The orthopedic sector continues to adopt 3D printing for a growing range of applications—in part because AM systems are becoming more affordable and can produce parts more quickly than before. Used initially for spine applications, AM is now accepted across multiple platforms, including more critical applications in orthopedics such as tibial trays and femoral implants.
“The trends we see are directly related to the markets in which our clients serve,” said Brian McLaughlin, president of Amplify Additive, a Scarborough, Maine-based provider of additive manufacturing for titanium orthopedic implants. “If you are a spine company, you need to have a 3D-printed solution to stay competitive. Uncemented solutions for total joints continue to grow, which means more 3D-printed tibial trays for total knees. I think that 3D-printed acetabular cups are also to be expected in today’s market.”
There is growing interest in metal binder jet printing, especially for titanium. Binder jet printing is similar to MIM and offers a competitive alternative for certain high-volume applications. Binder jet printing is not a mature market yet—however, in December 2020, Ex One announced its binder jet 3D printing system that allows reactive materials to be processed, including metals; a controlled-atmosphere model of its X1 160Pro extra-large production metal printer will be available in 2022 for aluminum and titanium production.1
MIM versus Metal AM
Compared to plastic components, metal as a raw material is costly to manufacture and there are many processes available for fabricating metal components. “The least expensive component is usually the raw materials,” said Santoro. “When additional steps are added, costs rise. The key is to pick the best process for each component. Having detailed knowledge of the costs and processing associated with as many of these technologies as possible makes the job easier.”
Metal injection molding combines plastic injection molding with metal powder fusion. MIM is often the method of choice when small or complex parts are required that cannot be efficiently manufactured using any other methods. Injection molding can be automated when high volumes and consistent quality are needed. “MIM is ideal for small, complex geometries and intricately-shaped parts,” said Santoro. “Post-MIM computer numerical control [CNC] machining can be used to achieve tight tolerances.”2
MIM parts are strong and can be bent, welded, hardened, and heat-treated like other wrought materials. A wide variety of metals can be processed with MIM, including stainless steel, steel alloys, iron-nickel alloys, cobalt alloys, tungsten alloys, and ceramics.
Since only a single mold is required to make a part using MIM, the process is highly repeatable and produces parts consistent in size, shape, and strength. Finished parts are relatively strong for their size, often above 95 percent density. According to Fast Radius, a Chicago, Ill.-based contract manufacturer that provides both AM and MIM services to the medical device industry, “because molds can cost anywhere from $50,000 to $100,000, which could be prohibitively expensive for low-volume production runs, MIM makes financial sense for annual volumes over 50,000 with a long production lifecycle.”3
Both MIM and 3MP have surface finishes that, in their raw states, are inferior to machined components. In addition, dimensional control can often be an issue. “In the raw state, MIM surface finish and dimension control are superior to those of 3MP,” said Eidem. “Many MIM and 3MP manufacturers have secondary machining and surface finishing capabilities that can close the gap between these two technologies.”
MIM typically comes with a longer qualification timeline when compared to other manufacturing processes. “Design iterations can also stretch timelines and budgets,” continued Eidem. “Because of this, OEMs often default to machined components and forego the long-term cost benefit of MIM. OEMs are constantly looking for ways to reduce this qualification timeline and iteration process to capitalize on the advantages of MIM. 3MP can be used to drastically reduce this timeline and iteration process.”
For example, Advanced Powder Products has its own 3D printing technology, Printalloy, that uses the same MIM powder and processing conditions as production components, without the need for tooling. This allows the engineering team to run experiments prior to production tooling being built. “These experiments help develop the process concurrently, saving time and increasing qualification speed,” said Eidem.
Engineers often use metal AM when they need to create specialized parts that require high-strength characteristics or have intricate design features. Metal AM does not require molds, which provides designers with more creative possibilities for shape, tolerance, and functionality. The main advantage of powder bed fusion is its ability to produce complex lattice and porous structures. These types of complex structures cannot be achieved using MIM or other manufacturing processes. However, the disadvantages of PBF are higher cost-per-part and lower volume production capability.
“Conversely, the advantage of MIM is that it is cost-effective and can produce high volumes,” said Kircher. “Products with complex structures are best suited to PBF, whereas simpler structures in need of high-volume production are better suited to MIM.”
Another important advancement in laser powder bed fusion technology is the development and deployment of programmable lasers as the power source. Instead of using a focused columnar laser, the density of the laser energy can be distributed into a shape such as a ring. “This advancement allows for significant increases in manufacturing speed and will also enable manufacturers to print new alloys that were previously difficult or impossible to produce,” said Olson.
The biocompatibility of laser powder bed fusion methods has also improved due to the elimination of requirements for binders.
Software Advances
Additive manufacturing of implants and surgical instruments accelerates the product development lifecycle and lowers inventory costs compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. An area of advancement that has greatly enabled MDMs and their contract manufacturers to fully realize the advantages of PBF is the development of design software. “Advanced software enables the design and production of complex implants and instruments with very fine feature resolutions,” said Ruppert.
“The next generation in orthopedic implant designs will utilize highly advanced software programs and are mathematically driven,” said Adam Clark, CEO for Tangible Solutions, a Fairborn, Ohio-based contract manufacturer of 3D-printed titanium orthopedic implants. “Now that the sky is the limit with new software capabilities, customers are getting creative and turning dreams into intentionally functional models.”
Improvements in design software include image synthesis or rendering, residual stress analysis, and real-time build simulation, all integrated into one software product. Improvements in computing power, combined with clever software solutions, now allow designers to create structures with multiple layers of additional complexity.
For example, 3D Systems has made significant upgrades to its 3DXpert software product. Improvements to porous structure generation using a graphical model allow for rapid generation and adjustments to porous structures used in medical devices. “Build simulation has also improved dramatically in recent years, which decreases the number of iterations and improves first-time right yields,” said Ruppert.
Now that MDMs and CMs have become deeply experienced with the laser powder bed fusion process, they are much better at predicting outcomes, which shortens the development cycle. As a result, engineers can evaluate designs for manufacturability, make necessary adjustments, and implement new product lines relatively quickly. “In contrast, with metal injection molding and binder jet printing, there is a lot more non-recurring engineering [NRE] and development that must happen during the development stage, because it involves de-binding and sintering processes that can introduce significant changes to the geometry of the part,” said Kircher. “It is an iterative process that creates the geometry needed in the final product. With PBF, you can go from prototype to finished part quickly. With MIM, however, NRE cost must be factored into the cost and project timelines.”
Another cost consideration with MIM is tooling. For example, many medical engineers think titanium MIM is prohibitively expensive, especially upfront tooling. However, for high-volume MIM applications, tooling costs are generally not a barrier—they are typically recovered within the first year of production due to part price savings. “Titanium MIM is in a class of its own for small parts in high volumes above 10,000 pieces annually,” said Mark Mielke, vice president of sales and marketing for Praxis Technology, a Queensbury, N.Y.-based provider of titanium metal injection molding. “AM is leading when it comes to prototyping and larger parts, especially in low volumes.”
Combining Forces
Metal injection molding and metal AM are not truly competitive processes because they address different application spaces within the medical device market. “MIM is better suited for higher-volume small parts, but it is less precise,” said Ruppert. “You cannot achieve the same isotropic values as you can with AM. Metal AM is better for producing larger, fine-featured parts that deliver the best mechanical properties.”
During product development, companies can become too machine-focused. When MDMs start designing, they may design more for the output of the machine process instead of designing for clinical achievements. Engineers may not realize that, even though metal AM and MIM are distinctly different methods that have their own preferred production scenarios, they can complement each other nicely when producing multiple parts and/or instrumentation for an entire implant system.
“When producing a new implant system, there are guides, instruments, cases, and packaging that go with the implants,” said Troy Olson, director of operations for the additive manufacturing division at rms Company. “Having the capabilities of both PBF and MIM to create these different pieces can reduce system launch time. If you know the best way to manufacture each component in an entire implant system, and have the capability to do so, the two methods complement each other well. You can also help the OEM choose the best manufacturing solution for its needs.”
Cobalt Extreme, an Australian company, has developed a process that builds a metallic endoskeleton using 3D printing and then injection molds a special polymer around that skeleton. Originally developed for oil field applications, the company realized it had potential for other markets, including medical devices.4
“The injection molded polymer in and around the metal endoskeleton is not conductive and becomes an insulator,” said David Nommensen, director of Cobalt Extreme. “In addition, other benefits of the injection-molded material include abrasion resistance, resilient deformability, cost, impact resistance, corrosion and chemical resistance, color, service temperature, and low weight. A metal endoskeleton adds mechanical strength to a polymer—think reinforced concrete.”4
Mitsubishi Chemical Advanced Materials, in partnership with AddiFab, a Danish company, has developed a new process called freeform injection molding, based on 3D-printed injection mold inserts. This allows injection molders to make the same types of products as 3D printing, but with the superior strength in finished parts that traditional injection molding provides.5
“Freeform injection molding creates injection-molded objects with the same design freedom offered by conventional 3D-printing,” said Lasse Staal, CEO for AddiFab. “At the same time, we have brought 3D-printing lead times and start-up costs to the injection molding industry, without compromising choice of materials.”5
The freeform injection molding process consists of five steps:
- A 3D model of the desired object is created
- A negative of the 3D model is created—the mold
- The mold is then 3D-printed using a proprietary 3D printable liquid photopolymer resin that can be dissolved completely
- The print is then placed in an injection molding machine and hot thermoplastic is pressed into the cavities of the print
- The print/injection combo is placed in a special solution that dissolves the print, leaving the completed injection molded part
This process could “be especially useful for rapid and inexpensive injection mold prototyping,” said Kerry Stevenson, founder of Fabbaloo, an additive manufacturing news source that tracks the latest developments in 3D printing and AM. “Normally, the process of injection molding first involves the creation of a metal mold, a very expensive and time-consuming process that is only worth doing if there is an expectation its cost will be defrayed over many thousands or even millions of units. This technology will make it possible to inexpensively produce objects virtually identical to proposed injection molded versions, without the cost of preparing the metal mold.”6
By keeping production costs down, the freeform injection molding process could allow a business to go into low-volume production for a product that later could be switched to a proper metal mold for mass production injection molding when demand calls for it. “Freeform injection molding works with not only thermoplastics, but also with metal injection molding and ceramics as well,” added Stevenson. “This opens up the possibility of using virtually the entire worldwide catalogs of such industrial materials in the process.”6
Medical device manufacturers can utilize a variety of methods for producing parts, medical devices, and instruments, including complex ones for surgical procedures such as laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery. According to Santoro, the key is to choose the best process for the component being created. MIM and metal AM each have their merits.
“A full-service contract manufacturing organization with a series of metal fabricating operations needed for surgical instruments, including critical cleaning operations, must contemplate several aspects, including cost, materials, and volume needed before determining which process will best meet the customer’s goals for each project,” said Santoro.
References
- bit.ly/mpo210741
- bit.ly/mpo210742
- bit.ly/mpo210743
- bit.ly/mpo210744
- bit.ly/mpo210745
- bit.ly/mpo210746
Mark Crawford is a full-time freelance business and marketing/communications writer based in Madison, Wis. His clients range from startups to global manufacturing leaders. He also writes a variety of feature articles for regional and national publications and is the author of five books.