Mark Crawford, Contributing Writer09.01.20
Computerized numerical control (CNC) machining is a critical manufacturing process for fabricating medical device parts and components. Equipment manufacturers continue to improve these machines to meet the ever-increasing performance metrics expected by the medical industry, especially those for an expanding array of minimally invasive surgical procedures. Therefore, medical device manufacturers (MDMs) are designing smaller and more complex devices with tighter tolerances. Engineers continue to push the limits of current machining technologies in their designs, asking for more capabilities and greater functionality. The urgency by MDMs to meet these needs is passed down through the supply chain to cutting tool manufacturers, robotics companies, and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software engineers to innovate and collaborate on machine solutions—and beat the competition to the market.
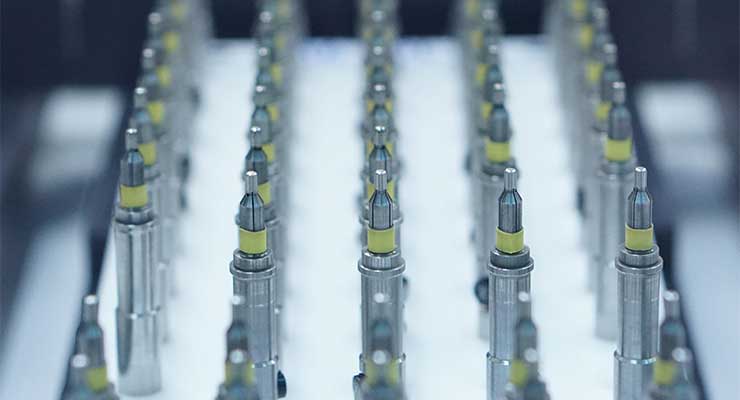
Automation and robotic-assisted CNC machining are a key focus because they improve efficiency, quality, and tolerance control. Advanced software continues to improve the automation of tasks such as welding, hole punching, and laser cutting. The efficiencies of automation help CNC machines stay competitive with additive manufacturing (AM) by manufacturing many of the complex shapes and extremely tight tolerances required for high-precision medical devices and durable complex parts. For example, high-volume machines can produce machine parts from 0.01 inches up to 1.25 inches in diameter, while holding tolerances as tight as 0.0002 inches for both turning and hole making.
“As the medical device industry continues to focus on improved patient outcomes, it is vital to have production processes that provide stringent, repeatable, precise, and accurate finished components,” said Ray DeFrain Jr., regional metallurgist for Carpenter Technology, a Philadelphia-based provider of high-performance alloy-based materials and process solutions for the medical device market. “Additionally, by linking these performance metrics with cost-down pressures of the industry at large, we see a shift toward lights-out manufacturing and Internet of Things [IoT] mobile control of multiple CNC cells.”
Latest Trends
MDMs are making a greater variety of micro-medical components with complicated features, which are typically processed with Swiss-style machining. They seek the speed, precision, reproducibility, and tight tolerances that these machines can provide. For example, “robotic surgical components are flooding our current requests,” said Craig Green, staff engineer for Cadence, a Staunton, Va.-based contract manufacturing partner that provides advanced products, technologies, and services to medical device and diagnostics companies. “These components are small, complicated, and in some cases, very delicate.”
Lasers are still one of hottest market segments in CNC machining—laser cutting, laser welding, laser texturing, and laser knurling. Combining laser processing with machining in hybrid equipment eliminates steps and saves time. For example, by combining laser cutting and welding with traditional Swiss turning, laser-Swiss machines can perform multiple processes in a single set-up, which can also streamline the validation process. The trend toward hybrid equipment also drives down costs by shortening lead times for prototyping and production volumes.
“Customers want to integrate these two processes into one platform to save on the assembly of individually machined and laser-cut parts,” said Damian Zyjeski, CNC production development manager for Okay Industries, a Berlin, Conn.-based manufacturer of medical device components and sub-assemblies. “Designers can expand the possibilities of having laser-cut features and machined features on the same part. This can sometimes replace traditional fully machined features, reducing cost and increasing quality.”
There is also a growing trend toward integrating robotic-assisted systems across two or more separate processes, “which reduces variability and allows greater process control,” said Tim Hoklas, senior director of technical solutions for Viant, a Foxborough, Mass.-based global outsource developer and manufacturer of medical devices and components. “In one of our facilities, we have incorporated four steps with one robot, with the flexibility to add more processes as needed. The part is laser machined, formed, laser cut, and inspected with the robot holding the part the whole time, resulting in fewer errors for part registration from process to process.”
Robotics incorporated into CNC machining and other hybrid technologies are also being used to collect and analyze data to improve process quality. CNC machines can now collect data in real time and control for factors such as thermal growth. These technologies are making greater use of algorithms that allow CNC machines to monitor temperature data, make adjustments, modify position, and resize around a product in production when needed. “The system can simply be programmed to accommodate part geometry, ensuring the accuracy of every part produced,” said John Cross, director of advanced machining for MICRO, a Somerset, N.J.-based full-service contract manufacturer of precision medical components, sub-assemblies, and complete devices for laparoscopic surgical procedures. “The technological advances that increase CNC’s utility in manufacturing are really exciting.”
More machinists are taking advantage of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tooling, which is fabricated from diamond particles sintered together with a metallic binder at extreme temperature and pressure. PCD tools are harder and more resistant to wear than standard carbide tools. Other benefits include longer tool life and more consistent results. Because they can run up to 10 times faster than solid carbide tools, PCD tools get the job done faster, boosting production volume and reducing lead times. PCD tools are especially useful for precious metal alloys, composites, and abrasive plastics, and can provide a high-quality surface finish, eliminating the need for secondary operations.
PCD tooling is also increasingly available in smaller sizes. “Advancements in PCD tooling capabilities at smaller sizes and in different configurations can perform a wider variety of operations than were possible 10 years ago and has increased our capabilities, enabling us to reduce multiple operations on different machines,” said Jason H. Smith, an associate development engineer for Johnson Matthey Medical Components, a San Diego, Calif.-based developer and manufacturer of precision micro-machined components for medical devices.
What OEMs Want
OEMs want higher quality standards, tighter tolerances, lower costs, and faster speed to market. They are always looking for solutions that can increase throughput and decrease scrap rates via material and process advancements, thereby reducing lead times and saving on cost.
They especially want more technical expertise and guidance from their contract manufacturers (CMs). OEMs are increasingly asking their CMs to collaborate on the development of new parts and products, including design, materials, prototyping, and testing, and expect them to have all the technical prowess they need to deliver the right solution, quickly.
“We work closely with our vendors to ensure availability and on-time delivery of tools used in new development set-ups,” said Smith.
Although MDMs may approach their contract manufacturers with a particular machining method in mind, most are open to suggestions that make more sense from a production viewpoint.
“Customers certainly want to be sure we have the capabilities and process controls in place,” said Hoklas. “But for many MDMs, it’s less about process and more about results. They might come to us with a particular process in mind for a component, but we may suggest something that’s a better match to their objectives. In one instance, we converted a machined part to a molded part and reduced the cost by 75 percent.”
To meet these increasingly wide variety of product requests, contract manufacturers must be creative with their existing equipment. “It’s not sustainable to purchase a machine tool for each and every technology, so we have to be innovative in our approach to processing parts with what we have,” said Green.
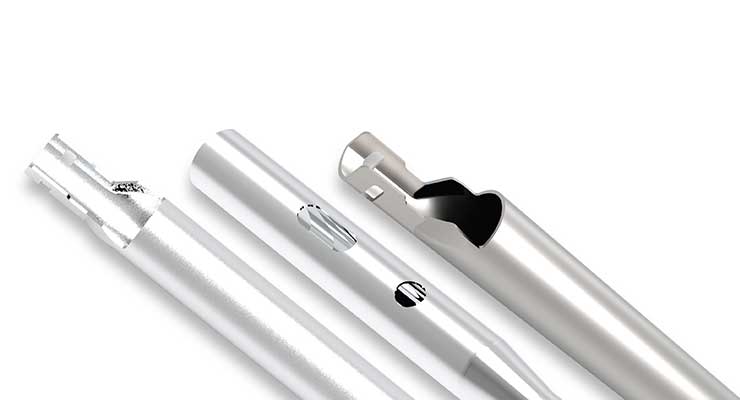
One of those product design challenges is the miniaturization of components and overall devices, in support of improved patient outcomes through minimally invasive surgeries. The complexity of these components requires sophisticated CNC machining know-how. Material advancements are just as important as machining advancements for the successful miniaturization of components. “Miniaturization requires advancements in both processing and materials,” said DeFrain. “For example, 17-4PH is a commonly used material that can be substituted with Custom 465 stainless as a drop-in replacement with increased strength and hardness, while still retaining very high levels of ductility and corrosion resistance.”
“MDMs looking to mass-produce components with complex features like diagonal cuts, shapes, and curves, and tight tolerances, will often opt for CNC,” said Cross. “The process achieves a high degree of accuracy for a wide range of finished parts, as well as rapid prototyping. In particular, CNC machines have a distinct advantage for production of metal devices and parts that require thermal conductivity and high strength and resistance.”
Technology Advancements
Low frequency vibration (LFV) cutting is a technique that helps reduce the formation of chips that cause scratches on surfaces, as well as unnecessary tool wear. Servo axes are vibrated in the axial direction as cutting is performed in sync with the rotation of the spindle, thereby ejecting chips intermittently. This method works especially well for products made from difficult-to-cut materials, such as stainless steel. LFV breaks chips into tiny pieces, which eliminates chip nesting and greatly reduces the need for high-pressure coolants. Using LFV also substantially increases throughput with less operator intervention and fewer machine stops due to tangled long chips.
New IoT-based sensing technologies can be placed on tools such as inserts and end mills to help maintain stability on challenging materials, such as titanium and polyether ether ketone (PEEK). Software can be installed on the machines that monitor load on specified tools in real time. “Limits are set for optimized performance and as soon as a tool becomes compromised, the limits are breached and the machine will stop and alert the operator or technician,” said Mario Chaves Jr., process development engineer for Okay Industries in Costa Rica.
Automation is also in high demand because of its obvious improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost—for example, it can reduce the need for operators and still run a process 24-7, all while monitoring performance and alerting staff when variance is detected in the production process.
Robot-enabled automation is increasingly used across two or more separate processes. “Every time you take the part out of a machine, you’re stacking up potential for error as you go from step to step,” said Hoklas. “With robotics, the part remains on one fixture across multiple operations, reducing variability and allowing greater process control.”
For example, a surgical technology customer approached Viant with an advanced energy device that required clamp-related tolerances to be tightened by up to 50 percent, which would require a technical leap forward in already extreme tolerances. “By integrating robot-assisted automation for CNC machining as well as other processes, we were able to reduce dimensional variation by 33 percent to improve clamp force, which delivered increased sealing strength and burst pressure,” said Hoklas.
Robotics can streamline the production system by minimizing human interaction. Adding robotic cells for material loading increases production throughput and speeds up turnaround time on machined components. Automated loading increases efficiency by reducing the time it takes to complete repetitive tasks, and it eliminates the element of human error.
“These systems are able to perform multiple precise tooling processes at a reduced cost, so production is more efficient without sacrificing on part quality,” said Cross. “Hybrid technology such as robotic cells incorporated into CNC machining is a trend that will likely continue to pick up traction.”
Okay Industries engineers build their own machines in-house, with an emphasis on automated loading and unloading. Robots are also used to do repetitive work. “This enables us to run ‘lights out’ in many cases, utilizing the equipment 24 hours a day,” said Zyjeski. “All our equipment uses sensors that not only improves quality and eliminates scrap, but also collects data we use for analyzing machine efficiency and capacity.” Machine monitoring software tracks up time and down time of the machines in the shop live. This data is then compared to standards to target improvements and develop capacity planning.
CNC machining relies on minimal run-out to ensure consistency, minimal user involvement, tight tolerances, and repeatability from piece-to-piece. Additionally, it is “Step 1” when considering lights-out manufacturing or off-site IoT controlled capability. For example, Carpenter Technology is currently developing a minimum residual stress 17-4PH bar stock for some unique medical CNC machining applications to ensure consistency from bar to bar.
“Ultimately, this will ensure minimal deflection during the machining operation and open the door to advanced, hands-off manufacturing of complex and thin-wall geometries,” said DeFrain.
“Furthermore, initial trial partners thought that secondary operations might be able to be eliminated due to first-time through acceptability. This would be a game-changer for many of the medical component machining practices, especially when it can be used for other alloys as well.”
Dimensional and positional tolerance on machined parts continues to tighten. True positions of features are commonly 0.001 inches or less; dimensional tolerances to 0.0005 inches or below are often required for new designs. Surface finish is becoming increasingly important for reducing friction between parts in assemblies.
“Surface finish requirements of 16 to 32 RMS are typical requirements,” said Zyjeski. “Machines with solid rigidity and higher spindle speeds of up to 40,000 RPM are often needed to produce fine cuts and eliminate tool marks. Post-machining surface treatments such as electropolish and fine media blasting can also be used to improve surface finish or meet customer design specifications.”
Extremely tight tolerances can be achieved with CNC machining. Swiss-turn machining has the capability to hold extremely tight tolerances while moving at high rates of speed on multiple axes, increasing productivity and reducing machining time. Spindle speeds are increasing to keep up with the shrinking size of parts and features. “The smaller the part features, the smaller the tool must be and the faster we have to run the spindle,” said Green. “It’s not uncommon to see the largest tool in the process be 0.032 inches.”
Swiss-turn machining and laser cutting can be combined for laser-cut slots and holes and simultaneous machining of differing outside diameters, which reduces set-up time, secondary processing, and handling costs.
“High-speed multi-axis milling CNC machines can also manufacture complex shapes with close tolerances required for high-precision medical device applications,” said Cross.
Moving Forward
CNC machines will continue to advance in the coming years and include improved chemical and processing control of raw materials, IoT, virtual reality, augmented reality, user interfaces, more axes, and software and cloud influences. For example, with sensor technologies and IoT wireless transmission, CNC machines can be operated remotely, running 24/7, without human interaction, maximizing quality and throughput. These improvements also help MDMs immensely with validation, tracking, regulatory compliance, and quality standards. Machining manufacturers are developing high-speed air spindles and higher-precision tooling to provide improved repeatability. Tooling continues to get smaller—for example, a 0.001-inch diameter endmill would not have been considered feasible 10 years ago.
Artificial intelligence also has a growing role, making the CNC machining process “smarter” as outputs are measured and communicated back to the equipment. “Software connects the machine to measuring equipment allowing pre-determined critical dimensions to be checked after that feature is completed,” said Zyjeski. “The inspection is done on each part as the machine is running. For instance, a critical turned diameter can be checked and tracked using statistical process control data and the machine will automatically offset the turning tool to keep the diameter within the control limits. This, along with tool lifecycle management, creates an extremely stable and high-quality process.”
Even though AM technology is becoming more capable in terms of materials and build size, it cannot yet compete with the speed and precision of Swiss screw machines. Also, many of the advanced materials or exotic alloys that can be CNC-machined cannot be processed through AM.
Although AM provides wonderful options for complex parts, internal features, and currently low-quantity components, “it cannot produce the tight tolerances, low surface roughness, or high quantities required by many applications,” said DeFrain. “Additionally, CNC machining is established with known performance standards—AM has a long road ahead with respect to adoption in critical components.”
However, it needs to be stated that CNC and AM are not mutually exclusive. As AM evolves, dual-purpose machines, called hybrid manufacturing, are emerging that incorporate AM build-up and CNC tolerances, speeds, and surface finishes in both series and parallel operations. “Feeding in a semi-finished component, and then performing both subtractive and additive manufacturing processes can leverage the best portions of each production methodology,” added DeFrain.
Rapidly evolving data capture and predictive analytics will enable highly predictive maintenance and monitor other key performance metrics that enhance the flexibility of CNC machining operations. Within minutes, a CNC machine can be reprogrammed to produce a different part or component. Designs can be stored in the control unit and easily revisited or adapted if a different part is required or there is a design change. These types of shifts can happen quickly and effortlessly, without unnecessary costs.
A common misconception with CNC machining, noted Cross, is that it will eventually replace human interface completely. Although it requires less human interaction, programmers are still needed to load the design into the software and a machinist is required to run the machine. An operator must also routinely monitor the machines to ensure they are working at the proper temperature, and parts and tools are in good working order. “The use of a highly automated process like CNC machining reduces the need for human personnel overall, which drives efficiencies, saves money, and improves safety in manufacturing,” said Cross.
Mark Crawford is a full-time freelance business and marketing/communications writer based in Madison, Wis. His clients range from startups to global manufacturing leaders. He also writes a variety of feature articles for regional and national publications and is the author of five books.
Automation and robotic-assisted CNC machining are a key focus because they improve efficiency, quality, and tolerance control. Advanced software continues to improve the automation of tasks such as welding, hole punching, and laser cutting. The efficiencies of automation help CNC machines stay competitive with additive manufacturing (AM) by manufacturing many of the complex shapes and extremely tight tolerances required for high-precision medical devices and durable complex parts. For example, high-volume machines can produce machine parts from 0.01 inches up to 1.25 inches in diameter, while holding tolerances as tight as 0.0002 inches for both turning and hole making.
“As the medical device industry continues to focus on improved patient outcomes, it is vital to have production processes that provide stringent, repeatable, precise, and accurate finished components,” said Ray DeFrain Jr., regional metallurgist for Carpenter Technology, a Philadelphia-based provider of high-performance alloy-based materials and process solutions for the medical device market. “Additionally, by linking these performance metrics with cost-down pressures of the industry at large, we see a shift toward lights-out manufacturing and Internet of Things [IoT] mobile control of multiple CNC cells.”
Latest Trends
MDMs are making a greater variety of micro-medical components with complicated features, which are typically processed with Swiss-style machining. They seek the speed, precision, reproducibility, and tight tolerances that these machines can provide. For example, “robotic surgical components are flooding our current requests,” said Craig Green, staff engineer for Cadence, a Staunton, Va.-based contract manufacturing partner that provides advanced products, technologies, and services to medical device and diagnostics companies. “These components are small, complicated, and in some cases, very delicate.”
Lasers are still one of hottest market segments in CNC machining—laser cutting, laser welding, laser texturing, and laser knurling. Combining laser processing with machining in hybrid equipment eliminates steps and saves time. For example, by combining laser cutting and welding with traditional Swiss turning, laser-Swiss machines can perform multiple processes in a single set-up, which can also streamline the validation process. The trend toward hybrid equipment also drives down costs by shortening lead times for prototyping and production volumes.
“Customers want to integrate these two processes into one platform to save on the assembly of individually machined and laser-cut parts,” said Damian Zyjeski, CNC production development manager for Okay Industries, a Berlin, Conn.-based manufacturer of medical device components and sub-assemblies. “Designers can expand the possibilities of having laser-cut features and machined features on the same part. This can sometimes replace traditional fully machined features, reducing cost and increasing quality.”
There is also a growing trend toward integrating robotic-assisted systems across two or more separate processes, “which reduces variability and allows greater process control,” said Tim Hoklas, senior director of technical solutions for Viant, a Foxborough, Mass.-based global outsource developer and manufacturer of medical devices and components. “In one of our facilities, we have incorporated four steps with one robot, with the flexibility to add more processes as needed. The part is laser machined, formed, laser cut, and inspected with the robot holding the part the whole time, resulting in fewer errors for part registration from process to process.”
Robotics incorporated into CNC machining and other hybrid technologies are also being used to collect and analyze data to improve process quality. CNC machines can now collect data in real time and control for factors such as thermal growth. These technologies are making greater use of algorithms that allow CNC machines to monitor temperature data, make adjustments, modify position, and resize around a product in production when needed. “The system can simply be programmed to accommodate part geometry, ensuring the accuracy of every part produced,” said John Cross, director of advanced machining for MICRO, a Somerset, N.J.-based full-service contract manufacturer of precision medical components, sub-assemblies, and complete devices for laparoscopic surgical procedures. “The technological advances that increase CNC’s utility in manufacturing are really exciting.”
More machinists are taking advantage of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tooling, which is fabricated from diamond particles sintered together with a metallic binder at extreme temperature and pressure. PCD tools are harder and more resistant to wear than standard carbide tools. Other benefits include longer tool life and more consistent results. Because they can run up to 10 times faster than solid carbide tools, PCD tools get the job done faster, boosting production volume and reducing lead times. PCD tools are especially useful for precious metal alloys, composites, and abrasive plastics, and can provide a high-quality surface finish, eliminating the need for secondary operations.
PCD tooling is also increasingly available in smaller sizes. “Advancements in PCD tooling capabilities at smaller sizes and in different configurations can perform a wider variety of operations than were possible 10 years ago and has increased our capabilities, enabling us to reduce multiple operations on different machines,” said Jason H. Smith, an associate development engineer for Johnson Matthey Medical Components, a San Diego, Calif.-based developer and manufacturer of precision micro-machined components for medical devices.
What OEMs Want
OEMs want higher quality standards, tighter tolerances, lower costs, and faster speed to market. They are always looking for solutions that can increase throughput and decrease scrap rates via material and process advancements, thereby reducing lead times and saving on cost.
They especially want more technical expertise and guidance from their contract manufacturers (CMs). OEMs are increasingly asking their CMs to collaborate on the development of new parts and products, including design, materials, prototyping, and testing, and expect them to have all the technical prowess they need to deliver the right solution, quickly.
“We work closely with our vendors to ensure availability and on-time delivery of tools used in new development set-ups,” said Smith.
Although MDMs may approach their contract manufacturers with a particular machining method in mind, most are open to suggestions that make more sense from a production viewpoint.
“Customers certainly want to be sure we have the capabilities and process controls in place,” said Hoklas. “But for many MDMs, it’s less about process and more about results. They might come to us with a particular process in mind for a component, but we may suggest something that’s a better match to their objectives. In one instance, we converted a machined part to a molded part and reduced the cost by 75 percent.”
To meet these increasingly wide variety of product requests, contract manufacturers must be creative with their existing equipment. “It’s not sustainable to purchase a machine tool for each and every technology, so we have to be innovative in our approach to processing parts with what we have,” said Green.
One of those product design challenges is the miniaturization of components and overall devices, in support of improved patient outcomes through minimally invasive surgeries. The complexity of these components requires sophisticated CNC machining know-how. Material advancements are just as important as machining advancements for the successful miniaturization of components. “Miniaturization requires advancements in both processing and materials,” said DeFrain. “For example, 17-4PH is a commonly used material that can be substituted with Custom 465 stainless as a drop-in replacement with increased strength and hardness, while still retaining very high levels of ductility and corrosion resistance.”
“MDMs looking to mass-produce components with complex features like diagonal cuts, shapes, and curves, and tight tolerances, will often opt for CNC,” said Cross. “The process achieves a high degree of accuracy for a wide range of finished parts, as well as rapid prototyping. In particular, CNC machines have a distinct advantage for production of metal devices and parts that require thermal conductivity and high strength and resistance.”
Technology Advancements
Low frequency vibration (LFV) cutting is a technique that helps reduce the formation of chips that cause scratches on surfaces, as well as unnecessary tool wear. Servo axes are vibrated in the axial direction as cutting is performed in sync with the rotation of the spindle, thereby ejecting chips intermittently. This method works especially well for products made from difficult-to-cut materials, such as stainless steel. LFV breaks chips into tiny pieces, which eliminates chip nesting and greatly reduces the need for high-pressure coolants. Using LFV also substantially increases throughput with less operator intervention and fewer machine stops due to tangled long chips.
New IoT-based sensing technologies can be placed on tools such as inserts and end mills to help maintain stability on challenging materials, such as titanium and polyether ether ketone (PEEK). Software can be installed on the machines that monitor load on specified tools in real time. “Limits are set for optimized performance and as soon as a tool becomes compromised, the limits are breached and the machine will stop and alert the operator or technician,” said Mario Chaves Jr., process development engineer for Okay Industries in Costa Rica.
Automation is also in high demand because of its obvious improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost—for example, it can reduce the need for operators and still run a process 24-7, all while monitoring performance and alerting staff when variance is detected in the production process.
Robot-enabled automation is increasingly used across two or more separate processes. “Every time you take the part out of a machine, you’re stacking up potential for error as you go from step to step,” said Hoklas. “With robotics, the part remains on one fixture across multiple operations, reducing variability and allowing greater process control.”
For example, a surgical technology customer approached Viant with an advanced energy device that required clamp-related tolerances to be tightened by up to 50 percent, which would require a technical leap forward in already extreme tolerances. “By integrating robot-assisted automation for CNC machining as well as other processes, we were able to reduce dimensional variation by 33 percent to improve clamp force, which delivered increased sealing strength and burst pressure,” said Hoklas.
Robotics can streamline the production system by minimizing human interaction. Adding robotic cells for material loading increases production throughput and speeds up turnaround time on machined components. Automated loading increases efficiency by reducing the time it takes to complete repetitive tasks, and it eliminates the element of human error.
“These systems are able to perform multiple precise tooling processes at a reduced cost, so production is more efficient without sacrificing on part quality,” said Cross. “Hybrid technology such as robotic cells incorporated into CNC machining is a trend that will likely continue to pick up traction.”
Okay Industries engineers build their own machines in-house, with an emphasis on automated loading and unloading. Robots are also used to do repetitive work. “This enables us to run ‘lights out’ in many cases, utilizing the equipment 24 hours a day,” said Zyjeski. “All our equipment uses sensors that not only improves quality and eliminates scrap, but also collects data we use for analyzing machine efficiency and capacity.” Machine monitoring software tracks up time and down time of the machines in the shop live. This data is then compared to standards to target improvements and develop capacity planning.
CNC machining relies on minimal run-out to ensure consistency, minimal user involvement, tight tolerances, and repeatability from piece-to-piece. Additionally, it is “Step 1” when considering lights-out manufacturing or off-site IoT controlled capability. For example, Carpenter Technology is currently developing a minimum residual stress 17-4PH bar stock for some unique medical CNC machining applications to ensure consistency from bar to bar.
“Ultimately, this will ensure minimal deflection during the machining operation and open the door to advanced, hands-off manufacturing of complex and thin-wall geometries,” said DeFrain.
“Furthermore, initial trial partners thought that secondary operations might be able to be eliminated due to first-time through acceptability. This would be a game-changer for many of the medical component machining practices, especially when it can be used for other alloys as well.”
Dimensional and positional tolerance on machined parts continues to tighten. True positions of features are commonly 0.001 inches or less; dimensional tolerances to 0.0005 inches or below are often required for new designs. Surface finish is becoming increasingly important for reducing friction between parts in assemblies.
“Surface finish requirements of 16 to 32 RMS are typical requirements,” said Zyjeski. “Machines with solid rigidity and higher spindle speeds of up to 40,000 RPM are often needed to produce fine cuts and eliminate tool marks. Post-machining surface treatments such as electropolish and fine media blasting can also be used to improve surface finish or meet customer design specifications.”
Extremely tight tolerances can be achieved with CNC machining. Swiss-turn machining has the capability to hold extremely tight tolerances while moving at high rates of speed on multiple axes, increasing productivity and reducing machining time. Spindle speeds are increasing to keep up with the shrinking size of parts and features. “The smaller the part features, the smaller the tool must be and the faster we have to run the spindle,” said Green. “It’s not uncommon to see the largest tool in the process be 0.032 inches.”
Swiss-turn machining and laser cutting can be combined for laser-cut slots and holes and simultaneous machining of differing outside diameters, which reduces set-up time, secondary processing, and handling costs.
“High-speed multi-axis milling CNC machines can also manufacture complex shapes with close tolerances required for high-precision medical device applications,” said Cross.
Moving Forward
CNC machines will continue to advance in the coming years and include improved chemical and processing control of raw materials, IoT, virtual reality, augmented reality, user interfaces, more axes, and software and cloud influences. For example, with sensor technologies and IoT wireless transmission, CNC machines can be operated remotely, running 24/7, without human interaction, maximizing quality and throughput. These improvements also help MDMs immensely with validation, tracking, regulatory compliance, and quality standards. Machining manufacturers are developing high-speed air spindles and higher-precision tooling to provide improved repeatability. Tooling continues to get smaller—for example, a 0.001-inch diameter endmill would not have been considered feasible 10 years ago.
Artificial intelligence also has a growing role, making the CNC machining process “smarter” as outputs are measured and communicated back to the equipment. “Software connects the machine to measuring equipment allowing pre-determined critical dimensions to be checked after that feature is completed,” said Zyjeski. “The inspection is done on each part as the machine is running. For instance, a critical turned diameter can be checked and tracked using statistical process control data and the machine will automatically offset the turning tool to keep the diameter within the control limits. This, along with tool lifecycle management, creates an extremely stable and high-quality process.”
Even though AM technology is becoming more capable in terms of materials and build size, it cannot yet compete with the speed and precision of Swiss screw machines. Also, many of the advanced materials or exotic alloys that can be CNC-machined cannot be processed through AM.
Although AM provides wonderful options for complex parts, internal features, and currently low-quantity components, “it cannot produce the tight tolerances, low surface roughness, or high quantities required by many applications,” said DeFrain. “Additionally, CNC machining is established with known performance standards—AM has a long road ahead with respect to adoption in critical components.”
However, it needs to be stated that CNC and AM are not mutually exclusive. As AM evolves, dual-purpose machines, called hybrid manufacturing, are emerging that incorporate AM build-up and CNC tolerances, speeds, and surface finishes in both series and parallel operations. “Feeding in a semi-finished component, and then performing both subtractive and additive manufacturing processes can leverage the best portions of each production methodology,” added DeFrain.
Rapidly evolving data capture and predictive analytics will enable highly predictive maintenance and monitor other key performance metrics that enhance the flexibility of CNC machining operations. Within minutes, a CNC machine can be reprogrammed to produce a different part or component. Designs can be stored in the control unit and easily revisited or adapted if a different part is required or there is a design change. These types of shifts can happen quickly and effortlessly, without unnecessary costs.
A common misconception with CNC machining, noted Cross, is that it will eventually replace human interface completely. Although it requires less human interaction, programmers are still needed to load the design into the software and a machinist is required to run the machine. An operator must also routinely monitor the machines to ensure they are working at the proper temperature, and parts and tools are in good working order. “The use of a highly automated process like CNC machining reduces the need for human personnel overall, which drives efficiencies, saves money, and improves safety in manufacturing,” said Cross.
Mark Crawford is a full-time freelance business and marketing/communications writer based in Madison, Wis. His clients range from startups to global manufacturing leaders. He also writes a variety of feature articles for regional and national publications and is the author of five books.