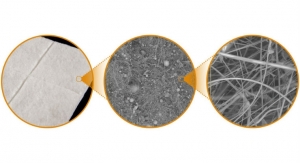
Rick Crane, Vice President of Innovation Services Group, J-Pac Medical10.12.16
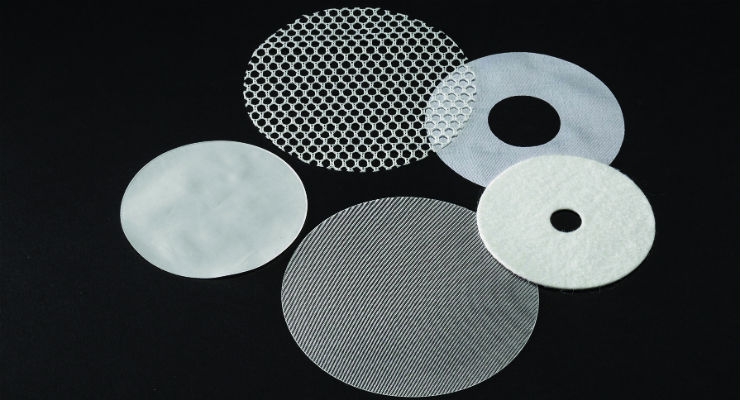
Medical-grade textiles are an ideal component for implantable medical devices, largely due to the product design versatility they offer. Textiles can be developed in 2D and 3D implantable forms in any number of configurations. Taking a raw textile material, however, and transforming it into an optimal medical implant is a complex process requiring a special combination of capabilities and materials expertise.
Understanding the most important factors that go into implant manufacturing can help OEMs ensure that the best final product is designed to meet the needs of their end user. Finding a single source to oversee devices from inception to manufacturing through packaging and sterilization reduces the complexity and likelihood of human error due to having multiple partners involved across the supply chain.
The applications in which implantable textiles play a part is extensive, and their presence is growing in conjunction with the infusion of new polymers, constructions, and the potential for more “active” device forms like drug/device combination products. Such products are typical in the sports medicine, trauma, orthopedics, wound management, tissue replacement, plastic surgery, neural, and endoscopy market segments.
A product list would include:
Manufacturing Implantable Textile Devices
Implantable textile devices can be created using resorbable or non-resorbable polymers, or a combination of different materials, and custom shaped to meet specific anatomical and biological requirements, as well as facilitate shape transformation in vivo.

The benefits of choosing the right partner to manufacture implantable textile devices include the ability to form and assemble complex 2D and 3D shapes.
Although textile structures have been used in certain surgical procedures for decades, increasing complexity driven by technology innovations are allowing textile devices to serve greater purposes and be an option for a broader range of applications. Having a clear understanding of the anatomical purpose of the device early on helps drive more informed decisions in the materials selection process, which will significantly impact design and development.
A combination of forming, cutting, and assembly capabilities for biomedical textiles supported by extensive materials handling expertise is needed to create 2D or 3D shapes with woven, knitted, braided, or non-woven textiles, films, and more. There are also multiple factors that need to be considered in the manufacturing process to ensure optimized implants that will provide maximum benefit to the end-user patient.
Correctness of the Shape
Today, the range of implantable textile constructs can be custom shaped in a wide variety of ways to meet specific anatomical and biological requirements. Customization of the implant’s shape by the manufacturer can reduce surgical procedure time by minimizing or eliminating currently needed intraoperative adjustments, and can also provide surgical repairs with reductions in tension inherent with non-customized implants. The value of a pre-shaped textile implant has been most notably demonstrated in the area of hernia repair, but potential applications exist more broadly across general, cardiovascular, and orthopedic surgical applications. A broadly capable manufacturing partner who understands the unique needs of different surgical applications can offer strategic counsel in the product development phase, and tooled with the necessary process capabilities—precision cutting, shaping, forming, and assembly capabilities during manufacturing—can optimize implant performance for purpose.
Specialized textile engineering techniques enable device developers to capitalize on the unique properties of different materials. Processes such as braiding, weaving, knitting, and non-woven help increase strength, texture, flexibility, and other performance characteristics for customized device requirements. For engineers, the possibilities for improved mechanical performance and anatomical accuracy are limitless, which will ultimately benefit the patient.
Interface to Instrumentation to Support Minimally Invasive Methodologies
A textile-based implant is only completed when it is coupled with a methodology to place the device properly in vivo in the most minimally invasive manner possible. In meeting this objective, it is sometimes necessary to add attachments to what will be the final implant that will interface effectively with needed instrumentation. These attachments to the implant are removed post-implantation, but nonetheless, are critical to an optimized implantation procedure.
The same cutting, shaping, and forming capabilities that drive the manufacture of an anatomically correct textile implant can also support this critical instrument integration and needed deployment features that can minimize the invasiveness of any given implantation method.
Benefits of Customized Edge Treatments
Most textiles are produced in a bulk form that provides a manufacturer with a desired material that is not necessarily in the desired unit-of-use configuration. These forms can be rolls, sheets, or reels of all sorts of multi-filament woven, knitted, or braided textiles. Traditional cutting processes are capable of providing a unit/part with the proper length or outline but in a manner that could cause the ends of textiles to fray, making the edges of the implant rough and potentially generating particulate or degrading the textile’s structural integrity. Cutting methods are available that will create semi-sealed edges on cut parts that drastically reduce the amount of particulate, and enhance the “surgical hand” of the implant by creating smoother, more flexible, cleaner, and more structurally stable implants with improved tissue passage characteristics that benefit both the patient and the surgical team.
Optimized edge treatment processes during manufacturing can offer broader benefits that may include:
One of the greatest benefits of implantable textile devices is that they can be patient-specific and developed for specialized end-user needs. Devices can be created entirely of absorbable components or of a combination of resorbable and non-resorbable parts. They can even be used for controlled delivery of drug or biological agents directly at the site of implantation.
It is important to choose the right textile materials and manufacturing partner to optimize the performance of the finished device for its intended purpose. A team that has the expertise to work with different kinds of materials—even hard-to-handle materials—and incorporate multiple materials into a device when beneficial will result in more optimized implants. Using thermal processing capabilities as a foundation for material manipulation, supported by a blend of tooling, materials, automation, and process expertise will result in more innovative solutions to complex customer challenges.
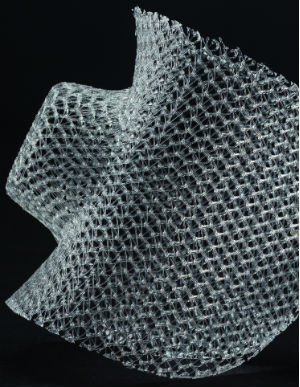
Resorbable and non-resorbable polymers can be used to create implantable textile devices that are custom-shaped to meet specific anatomical and biological requirements, as well as facilitate shape transformation in vivo.
In instances where resorbable and/or lyophilized materials are included in the implant, the manufacturer should utilize low humidity cleanroom manufacturing environments (dry rooms) to extend the WIP Time (open exposure time) for materials and components that are moisture-sensitive, and also to drive product consistency that can be impacted by uncontrolled humidity. Production controls should also be in place to negate any product impact that can be brought on by overexposure to humidity.
Benefits of Resorbable Implants
Generic textile implants that merely provide the infrastructure for the healing process have the potential to be replaced by active textile implants that can actually play a critical role in the wound healing process. Implants using resorbable textiles break down naturally in the body after a procedure, which can help support improved clinical outcomes, and reduce costs by eliminating foreign materials in the body or the need for additional implant removal procedures. These implants can be customized to unique anatomical shapes and incorporate various coatings that can help direct the healing process and reduce potential complications. Additionally, resorbable textile implants don’t interfere with imaging and radiotherapy like other permanent implants may.
Resorbable textile implants have gained a foothold in the orthopedics market as a well-suited option to aid in tissue regeneration and strength-building at the surgical site. As polymer and textile-based implants are being perfected through optimized manufacturing processes to overcome strength limitations and other adoption barriers, they are increasingly being recognized as viable—often superior—options in other medical application markets, too. The adhesion prevention qualities that can be applied to textiles are highly beneficial for women’s health applications, for example.
Packaging and Sterilization
Value-added packaging is an integral part of any finished implant. For implants that incorporate resorbable materials, the packaging must provide the necessary barrier to ensure efficacy over the claimed shelf life. These barrier put-ups may also incorporate modified atmosphere (gas-flushed) packaging in order to extend shelf life, and/or can include desiccants and scavengers to gain the same outcome.
For implants that incorporate a 3D shape, the package must protect and maintain the desired anatomical shape. The package must not only protect the implant through distribution and while on the shelf, but also provide an intuitive and convenient platform to support sterile delivery technique in the OR.
If the implant is provided with instruments to be used during implantation, the packaging also needs to support the intended use of these instruments and aid the nurse and surgeon to gain easy access in the order items are needed.
In instances where actives and/or a combination of resorbable and non-resorbable polymers are in use in a single device, a package format and flow may need to be developed to accommodate multiple sterilization flows such that each polymer chemistry present is sterilized in a manner not detrimental to its performance. In some cases, it may be necessary to perform separate sterilization flows for various components of the implant that are mated downstream in the supply chain to assemble the final kit. While these instances are not common currently, they will become more relevant as actives (drug/device combinations) are incorporated into the textile implants.
Conclusion
Surgical repairs relying on medical grade textiles are in a transition. The optimization of the implant for surgical use is being pushed back into the manufacturing process, and out of the operating room. More reliance is being placed on the manufacturer to provide a device that is ready to implant with minimum or no revision by the surgeon. This requires a gambit of competencies, many of which have been mentioned in this article. Additionally, the implants are becoming chemically interactive with body chemistries as the devices take on resorbable characteristics, or are a drug/device combination. These requirements and trends are creating a specialized set of needs for those OEMs seeking a qualified manufacturer of textile-based implants. Contrarily, the trends are also creating an opportunity for those companies that can provide the unique set of capabilities needed to manufacture, package, and sterilize a textile-based implant in today’s medical device marketplace.
There exists a broad set of requirements to be considered in the effort to develop and implement an optimized textile implant. The situation is complicated further by the integrated nature of polymer/construction textile-related decisions that will be made based on the surgical repair, and then the blending of the overlayed implantation methodology requirements, not to mention the resulting packaging/sterilization requirements. The approaching incorporation of actives into the textile construct will establish another angle to be considered.
When considering a manufacturer for a medical textile implant, consider all the aspects that have been presented here. With the large number of integrated potential issues, try to identify a supplier that has experience with all aspects of medical textile device manufacturing, including packaging and sterilization. If the product incorporates resorbable materials or components, consider those additional specialized requirements as well. The selection of the right manufacturing partner can pay dividends through the entire product lifecycle.
Rick Crane has more than 30 years of experience in the healthcare products industry. He brings strong general management skills demonstrated across operations, R&D, program management, technical sales, and marketing organizations. Crane has been instrumental in the development of J-Pac Medical’s Innovation Services Group and utilizes his product development and operational experiences to identify those capabilities and services that can most benefit J-Pac Medical’s customers.
Understanding the most important factors that go into implant manufacturing can help OEMs ensure that the best final product is designed to meet the needs of their end user. Finding a single source to oversee devices from inception to manufacturing through packaging and sterilization reduces the complexity and likelihood of human error due to having multiple partners involved across the supply chain.
The applications in which implantable textiles play a part is extensive, and their presence is growing in conjunction with the infusion of new polymers, constructions, and the potential for more “active” device forms like drug/device combination products. Such products are typical in the sports medicine, trauma, orthopedics, wound management, tissue replacement, plastic surgery, neural, and endoscopy market segments.
A product list would include:
- Hernia repair products
- Nerve conduits
- Cardiovascular plugs
- Heart valve sewing cuffs
- Collapsible orthopedic anchors
- Diabetic wound care tissue scaffolds
- Osteoconductive bone grafts
- Scoliosis correction devices
- Suture loops
- Sternal closure devices
- Partially to fully resorbable soft tissue repair products
- Drug and device combination products
Manufacturing Implantable Textile Devices
Implantable textile devices can be created using resorbable or non-resorbable polymers, or a combination of different materials, and custom shaped to meet specific anatomical and biological requirements, as well as facilitate shape transformation in vivo.

The benefits of choosing the right partner to manufacture implantable textile devices include the ability to form and assemble complex 2D and 3D shapes.
A combination of forming, cutting, and assembly capabilities for biomedical textiles supported by extensive materials handling expertise is needed to create 2D or 3D shapes with woven, knitted, braided, or non-woven textiles, films, and more. There are also multiple factors that need to be considered in the manufacturing process to ensure optimized implants that will provide maximum benefit to the end-user patient.
Correctness of the Shape
Today, the range of implantable textile constructs can be custom shaped in a wide variety of ways to meet specific anatomical and biological requirements. Customization of the implant’s shape by the manufacturer can reduce surgical procedure time by minimizing or eliminating currently needed intraoperative adjustments, and can also provide surgical repairs with reductions in tension inherent with non-customized implants. The value of a pre-shaped textile implant has been most notably demonstrated in the area of hernia repair, but potential applications exist more broadly across general, cardiovascular, and orthopedic surgical applications. A broadly capable manufacturing partner who understands the unique needs of different surgical applications can offer strategic counsel in the product development phase, and tooled with the necessary process capabilities—precision cutting, shaping, forming, and assembly capabilities during manufacturing—can optimize implant performance for purpose.
Specialized textile engineering techniques enable device developers to capitalize on the unique properties of different materials. Processes such as braiding, weaving, knitting, and non-woven help increase strength, texture, flexibility, and other performance characteristics for customized device requirements. For engineers, the possibilities for improved mechanical performance and anatomical accuracy are limitless, which will ultimately benefit the patient.
Interface to Instrumentation to Support Minimally Invasive Methodologies
A textile-based implant is only completed when it is coupled with a methodology to place the device properly in vivo in the most minimally invasive manner possible. In meeting this objective, it is sometimes necessary to add attachments to what will be the final implant that will interface effectively with needed instrumentation. These attachments to the implant are removed post-implantation, but nonetheless, are critical to an optimized implantation procedure.
The same cutting, shaping, and forming capabilities that drive the manufacture of an anatomically correct textile implant can also support this critical instrument integration and needed deployment features that can minimize the invasiveness of any given implantation method.
Benefits of Customized Edge Treatments
Most textiles are produced in a bulk form that provides a manufacturer with a desired material that is not necessarily in the desired unit-of-use configuration. These forms can be rolls, sheets, or reels of all sorts of multi-filament woven, knitted, or braided textiles. Traditional cutting processes are capable of providing a unit/part with the proper length or outline but in a manner that could cause the ends of textiles to fray, making the edges of the implant rough and potentially generating particulate or degrading the textile’s structural integrity. Cutting methods are available that will create semi-sealed edges on cut parts that drastically reduce the amount of particulate, and enhance the “surgical hand” of the implant by creating smoother, more flexible, cleaner, and more structurally stable implants with improved tissue passage characteristics that benefit both the patient and the surgical team.
Optimized edge treatment processes during manufacturing can offer broader benefits that may include:
- Enhanced edge quality of implantable medical textiles, which may minimize tissue inflammation and scar tissue formation
- Reinforced edge feature that can enhance stability and suture pull-out
- An integrated deployment feature that can enable device delivery through cannula
- A smoother edge to enhance tissue passage
- Advance manufacturability of the finished device, which reduces component preparation time within the overall device assembly process
One of the greatest benefits of implantable textile devices is that they can be patient-specific and developed for specialized end-user needs. Devices can be created entirely of absorbable components or of a combination of resorbable and non-resorbable parts. They can even be used for controlled delivery of drug or biological agents directly at the site of implantation.
It is important to choose the right textile materials and manufacturing partner to optimize the performance of the finished device for its intended purpose. A team that has the expertise to work with different kinds of materials—even hard-to-handle materials—and incorporate multiple materials into a device when beneficial will result in more optimized implants. Using thermal processing capabilities as a foundation for material manipulation, supported by a blend of tooling, materials, automation, and process expertise will result in more innovative solutions to complex customer challenges.

Resorbable and non-resorbable polymers can be used to create implantable textile devices that are custom-shaped to meet specific anatomical and biological requirements, as well as facilitate shape transformation in vivo.
Benefits of Resorbable Implants
Generic textile implants that merely provide the infrastructure for the healing process have the potential to be replaced by active textile implants that can actually play a critical role in the wound healing process. Implants using resorbable textiles break down naturally in the body after a procedure, which can help support improved clinical outcomes, and reduce costs by eliminating foreign materials in the body or the need for additional implant removal procedures. These implants can be customized to unique anatomical shapes and incorporate various coatings that can help direct the healing process and reduce potential complications. Additionally, resorbable textile implants don’t interfere with imaging and radiotherapy like other permanent implants may.
Resorbable textile implants have gained a foothold in the orthopedics market as a well-suited option to aid in tissue regeneration and strength-building at the surgical site. As polymer and textile-based implants are being perfected through optimized manufacturing processes to overcome strength limitations and other adoption barriers, they are increasingly being recognized as viable—often superior—options in other medical application markets, too. The adhesion prevention qualities that can be applied to textiles are highly beneficial for women’s health applications, for example.
Packaging and Sterilization
Value-added packaging is an integral part of any finished implant. For implants that incorporate resorbable materials, the packaging must provide the necessary barrier to ensure efficacy over the claimed shelf life. These barrier put-ups may also incorporate modified atmosphere (gas-flushed) packaging in order to extend shelf life, and/or can include desiccants and scavengers to gain the same outcome.
For implants that incorporate a 3D shape, the package must protect and maintain the desired anatomical shape. The package must not only protect the implant through distribution and while on the shelf, but also provide an intuitive and convenient platform to support sterile delivery technique in the OR.
If the implant is provided with instruments to be used during implantation, the packaging also needs to support the intended use of these instruments and aid the nurse and surgeon to gain easy access in the order items are needed.
In instances where actives and/or a combination of resorbable and non-resorbable polymers are in use in a single device, a package format and flow may need to be developed to accommodate multiple sterilization flows such that each polymer chemistry present is sterilized in a manner not detrimental to its performance. In some cases, it may be necessary to perform separate sterilization flows for various components of the implant that are mated downstream in the supply chain to assemble the final kit. While these instances are not common currently, they will become more relevant as actives (drug/device combinations) are incorporated into the textile implants.
Conclusion
Surgical repairs relying on medical grade textiles are in a transition. The optimization of the implant for surgical use is being pushed back into the manufacturing process, and out of the operating room. More reliance is being placed on the manufacturer to provide a device that is ready to implant with minimum or no revision by the surgeon. This requires a gambit of competencies, many of which have been mentioned in this article. Additionally, the implants are becoming chemically interactive with body chemistries as the devices take on resorbable characteristics, or are a drug/device combination. These requirements and trends are creating a specialized set of needs for those OEMs seeking a qualified manufacturer of textile-based implants. Contrarily, the trends are also creating an opportunity for those companies that can provide the unique set of capabilities needed to manufacture, package, and sterilize a textile-based implant in today’s medical device marketplace.
There exists a broad set of requirements to be considered in the effort to develop and implement an optimized textile implant. The situation is complicated further by the integrated nature of polymer/construction textile-related decisions that will be made based on the surgical repair, and then the blending of the overlayed implantation methodology requirements, not to mention the resulting packaging/sterilization requirements. The approaching incorporation of actives into the textile construct will establish another angle to be considered.
When considering a manufacturer for a medical textile implant, consider all the aspects that have been presented here. With the large number of integrated potential issues, try to identify a supplier that has experience with all aspects of medical textile device manufacturing, including packaging and sterilization. If the product incorporates resorbable materials or components, consider those additional specialized requirements as well. The selection of the right manufacturing partner can pay dividends through the entire product lifecycle.
Rick Crane has more than 30 years of experience in the healthcare products industry. He brings strong general management skills demonstrated across operations, R&D, program management, technical sales, and marketing organizations. Crane has been instrumental in the development of J-Pac Medical’s Innovation Services Group and utilizes his product development and operational experiences to identify those capabilities and services that can most benefit J-Pac Medical’s customers.