Association for Psychological Science12.06.17
When signals between the brain and one eye go awry, input from the other eye can become predominant, a condition called amblyopia or "lazy eye." Amblyopia is common and it is typically treated by forcing the less dominant eye to adapt, either through lab-based training or wearing an eyepatch. But new research suggests that people may be able to use wearable augmented-reality technology to reduce this visual discrepancy as they go about everyday activities.
The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
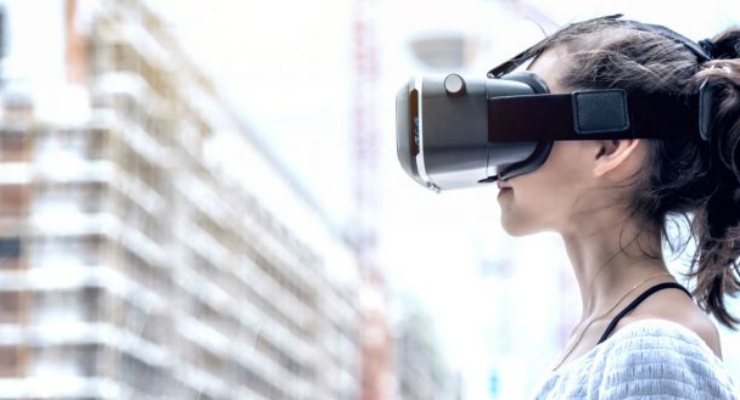
"With this altered-reality system, participants interact with the natural world that is changed through real-time image processing. The system delivers altered but complementary video to each eye in real time, forcing participants to make use of the visual inputs to both eyes cooperatively," explained lead researcher Min Bao of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The altered-reality system can be considered as a special type of the augmented-reality technology, in which some aspects of the scene are altered before the video is delivered to the observer but no unnatural and nonexistent object (e.g. an arrow or a web page) is superimposed. Using augmented reality to alter visual input in this way avoids some limitations of lab-based training:
"This method manipulates the visual world electronically so as to incorporate training into everyday life," said Bao.
And the findings showed that improvement in ocular balance endured over a 2-month follow-up period:
"Several 3-hour adaptation sessions produced effects that strengthened when people returned to their normal visual environment after the training ended," Bao explained.
In their first experiment, Bao and colleagues recruited 10 adult participants who showed significant interocular imbalance. During a 5-day adaptation stage, the participants had a daily 3-hour training session, in which they wore an augmented-reality headset that showed them a slightly altered version of their surrounding environment in real time. The images presented to each eye were identical except for unique patches that were pixelated in each image. The training essentially forced participants to weight the input from each eye equally to be able to process and perceive the complete scene. Participants completed the adaptation training sessions in the laboratory as they engaged in typical everyday activities, such as watching movies, playing video games, eating, and walking.
To gauge change in ocular dominance over time, the researchers had participants complete a binocular-rivalry task before the adaptation phase, at the beginning of each training session in the adaptation phase, and at follow-up sessions 24 hours, 2 days, 3 days, 1 week, 3 weeks, 2 months, and 4 months after the last training session. In each trial of the task, the participants saw two images simultaneously, one presented to each eye. Each image featured a striped grating pattern, with the pattern in one image oriented in a different direction from the pattern in the other image. After seeing the images, participants pressed a key to indicate the direction of the pattern they saw (tilted counterclockwise from vertical, tilted clockwise from vertical, or mixed).
When different images are presented to each eye, people tend to perceive the images as alternating back and forth and they typically report seeing the image presented to their dominant eye a greater proportion of the time. Thus, the task should reveal any changes in ocular dominance over time.
And participants did show training-related changes in ocular dominance over time. The results indicated that the stimuli shown to the stronger eye became less dominant over time, effectively increasing participants' interocular balance.
Importantly, interocular balance continued to improve in the 2 months after training ended and the researchers continued to observe training-related improvement at the 4-month follow-up.
In another experiment, 18 participants who were actually diagnosed with amblyopia participated in a similar training procedure. Again, they showed improvement throughout the training phase and in the weeks that followed. On average, their improvement in visual acuity was equivalent to being able to read an additional 1.5 lines down on the standard logMAR eye chart.
Findings from a third group of participants indicated that the weaker eye showed improvement in various functions—such as dichoptic motion coherence, visual acuity, and interocular phase combination—as a result of training.
Bao and colleagues first introduced this novel method for reshaping ocular dominance via augmented-reality technology at the annual conference of Vision Sciences Society in 2014. They believe their new findings could have important implications for work in a variety of domains, including clinical ophthalmology, neuroscience, engineering, and product development. They plan to continue this line of research, investigating the exact mechanisms that drive these training-related effects.
Find more information on the study here.
The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"With this altered-reality system, participants interact with the natural world that is changed through real-time image processing. The system delivers altered but complementary video to each eye in real time, forcing participants to make use of the visual inputs to both eyes cooperatively," explained lead researcher Min Bao of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The altered-reality system can be considered as a special type of the augmented-reality technology, in which some aspects of the scene are altered before the video is delivered to the observer but no unnatural and nonexistent object (e.g. an arrow or a web page) is superimposed. Using augmented reality to alter visual input in this way avoids some limitations of lab-based training:
"This method manipulates the visual world electronically so as to incorporate training into everyday life," said Bao.
And the findings showed that improvement in ocular balance endured over a 2-month follow-up period:
"Several 3-hour adaptation sessions produced effects that strengthened when people returned to their normal visual environment after the training ended," Bao explained.
In their first experiment, Bao and colleagues recruited 10 adult participants who showed significant interocular imbalance. During a 5-day adaptation stage, the participants had a daily 3-hour training session, in which they wore an augmented-reality headset that showed them a slightly altered version of their surrounding environment in real time. The images presented to each eye were identical except for unique patches that were pixelated in each image. The training essentially forced participants to weight the input from each eye equally to be able to process and perceive the complete scene. Participants completed the adaptation training sessions in the laboratory as they engaged in typical everyday activities, such as watching movies, playing video games, eating, and walking.
To gauge change in ocular dominance over time, the researchers had participants complete a binocular-rivalry task before the adaptation phase, at the beginning of each training session in the adaptation phase, and at follow-up sessions 24 hours, 2 days, 3 days, 1 week, 3 weeks, 2 months, and 4 months after the last training session. In each trial of the task, the participants saw two images simultaneously, one presented to each eye. Each image featured a striped grating pattern, with the pattern in one image oriented in a different direction from the pattern in the other image. After seeing the images, participants pressed a key to indicate the direction of the pattern they saw (tilted counterclockwise from vertical, tilted clockwise from vertical, or mixed).
When different images are presented to each eye, people tend to perceive the images as alternating back and forth and they typically report seeing the image presented to their dominant eye a greater proportion of the time. Thus, the task should reveal any changes in ocular dominance over time.
And participants did show training-related changes in ocular dominance over time. The results indicated that the stimuli shown to the stronger eye became less dominant over time, effectively increasing participants' interocular balance.
Importantly, interocular balance continued to improve in the 2 months after training ended and the researchers continued to observe training-related improvement at the 4-month follow-up.
In another experiment, 18 participants who were actually diagnosed with amblyopia participated in a similar training procedure. Again, they showed improvement throughout the training phase and in the weeks that followed. On average, their improvement in visual acuity was equivalent to being able to read an additional 1.5 lines down on the standard logMAR eye chart.
Findings from a third group of participants indicated that the weaker eye showed improvement in various functions—such as dichoptic motion coherence, visual acuity, and interocular phase combination—as a result of training.
Bao and colleagues first introduced this novel method for reshaping ocular dominance via augmented-reality technology at the annual conference of Vision Sciences Society in 2014. They believe their new findings could have important implications for work in a variety of domains, including clinical ophthalmology, neuroscience, engineering, and product development. They plan to continue this line of research, investigating the exact mechanisms that drive these training-related effects.
Find more information on the study here.